e-Invoicing mandates a strategic adjustment in business operations, aimed at fostering compliance and optimising management strategies, with its phased introduction starting August 1, 2024, for large taxpayers.
Set to become compulsory for all Malaysian taxpayers by July 1, 2025, the implementation of e-invoicing presents a pivotal opportunity for businesses to leverage technology for improved compliance and efficiency. This transition underscores the importance of understanding e-invoice regulations, system integration, and the benefits of adopting electronic invoicing solutions for seamless business operations and enhanced record-keeping practices.
Understanding e-Invoice LHDN
The transition to e-Invoicing in Malaysia introduces a significant shift in how businesses manage and report their transactions. Here’s a closer look at key aspects:
Types of e-Invoices
- e-Invoices are required for both proof of income and expenses, covering scenarios such as Business to Business (B2B), Business to Customer (B2C), and Business to Government (B2G) transactions.
- There are four types of e-Invoices: Invoices, Credit Notes, Debit Notes, and Refund Notes.
e-Invoicing Transmission
There are two main methods for sending e-invoices to the Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia (IRBM).
The first is through the MyInvois Portal, an online platform provided by IRBM for both individual and batch e-invoice generation. This method is free for all businesses. It requires manual data entry and enables business to generate, reject, or cancel invoices according to Malaysia’s e-invoicing requirements.
The second option is API integration, which is suitable for businesses, ERPs, and Peppol Access Point Providers. This method allows for the automatic processing and transmission of a large number of transactions.
While MyInvois is a good solution for businesses without the resources for API integration, it may not be ideal for larger taxpayers or high-volume businesses. In such cases, API integration offers the most convenient option.
For instance, whether your business already has an accounting system or not, the SWIF Payment Gateway & e-Invoice Plug-in facilitates direct data transmission between the taxpayer’s system and the MyInvois system, streamlining the process regardless of your existing infrastructure. SwiF ensures both data security and seamless system integration.
e-Invoice Process Flow
The e-Invoicing process involves six core steps: Issuance, Validation, Notification, Sharing, Rejection or Request for Cancellation, and Storage.
Issuance
After a sale or transaction agreement, your first step is to generate an invoice and share it with the IRBM via the MyInvois portal or through direct API integration such as SwiF.
Validation
Once validated in near real-time by the MyInvois Portal, the supplier will receive a validated e-Invoice which includes a Unique Identifier Number, date and time of validation, and validation link, allowing traceability of invoices.
Notification of validation
Once the e-Invoice has been validated with the Unique Identifier Number, IRBM will notify both the Supplier and Buyer via the MyInvois Portal or API response.
e-Invoice Sharing
Upon validation, the Supplier needs to share the validated e-Invoice with the Buyer embeded with the QR code provided by IRBM. The QR code enables both parties to validate the existence and status of the e-Invoice via the MyInvois Portal.
Rejection or Request for Cancellation
After validation by IRBM, both the Supplier and Buyer have a limited time to cancel or reject the e-Invoice.
- Buyer’s Rejection: If the e-Invoice has errors, the Buyer can request rejection within 72 hours via the MyInvois Portal, stating the reason.
- Supplier’s Cancellation: The Supplier can cancel the e-Invoice within 72 hours if it has errors or was issued erroneously, providing justifications.
Storage
IRBM will store all validated e-Invoices in its database. However, taxpayers should still maintain adequate records and documentation related to the transaction. The minimum archiving period for electronic invoices in Malaysia is 7 years.
By familiarising with these components, Malaysian businesses can ensure a seamless transition to e-Invoicing, aligning with regulatory compliance and enhancing operational efficiency.
Requirements
Digital Certificate
e-Invoicing in Malaysia, requires a Digital Certificate issued by IRBM, which is linked to the taxpayer’s Tax Identification Number (TIN). This certificate serves to authenticate the e-Invoice issuer’s identity and remains valid for a period of three years.
Information
A compliant e-invoice in Malaysia has 55 fields, 35 of them are mandatory and 20 optional. They include buyer and seller information, item or service description, payment details, total amount, etc.
Phased Implementation of e-Invoice LHDN
The phased implementation of e-Invoicing in Malaysia is designed to ensure a smooth transition for businesses across various sizes and sectors. This structured approach allows for adequate preparation time, system testing, and compliance alignment. Here’s a breakdown:
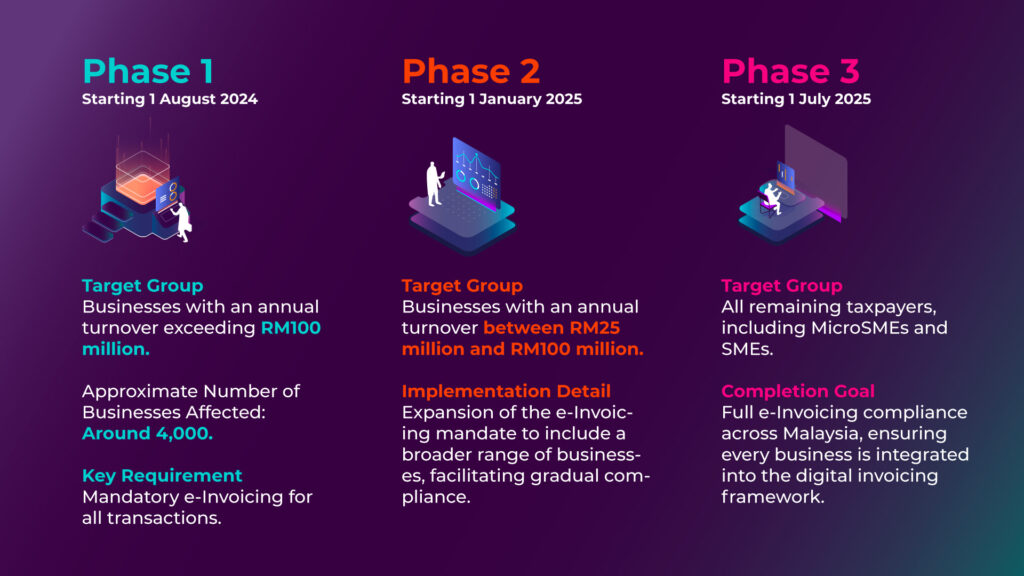
This phased approach underscores Malaysia’s commitment to digital transformation while providing businesses ample time to adapt, ensuring they meet the IRBM requirements through platforms like MyInvois Portal or direct API integration for seamless e-Invoice transmission.
Preparing Your Business for e-Invoice LHDN Adoption
Adapting to e-Invoicing in Malaysia requires a multifaceted approach, focusing on internal adjustments, compliance, and technological readiness. By embracing these changes, businesses can leverage e-Invoicing for improved efficiency, compliance, and growth.
Here are key steps to prepare your business for e-Invoice LHDN adoption:
Operational and Compliance Preparation
- Adapt internal business operations to seamlessly integrate e-Invoices, ensuring smooth transition and minimal disruption.
- Accounts Receivable (AR) and Accounts Payable (AP) functions will see significant changes, necessitating adjustments in invoice issuance, processing, and approval.
- Ensure full compliance with LHDN requirements through a thorough understanding of guidelines and mandates.
- Engage with e-Invoice events to stay informed on developments, allowing for timely adjustments to strategies.
Technological and Best Practices
- Assess e-Invoicing readiness and ensure software compatibility. This includes choosing the right integration model based on current system setup, operational requirements, and solution features.
- Select an experienced vendor for a reliable integration experience, focusing on data security and seamless system integration.
- Prepare for e-Invoicing launch by familiarising with the IRBM’s portal and setting aside an upfront investment solely for e-invoicing.
Overcoming Challenges and Strengthening Systems
- Address challenges such as regulatory compliance, technological transition, data security concerns, and resistance to change through strategic planning and stakeholder engagement.
- For businesses with multiple subsidiaries, unify financial information for consolidation by investing in strong unified financial systems, centralising financial teams, and leveraging technology.
- Upskill AR and AP teams, collate mandatory e-Invoice data fields, and establish clear reporting protocols to ensure data accuracy and regulatory compliance.
By following these guidelines, Malaysian businesses can navigate the complexities of e-Invoicing implementation, ensuring a smooth transition while maximising the benefits of electronic invoicing for enhanced business efficiency and compliance.
Conclusion
As Malaysian businesses approach the defined timelines for e-invoicing adoption, the emphasis on readiness strategy cannot be overstated. This encompasses technological preparedness, alignment with compliance mandates, and adaptation to operational changes, all of which are critical for a seamless transition. The journey toward e-invoicing adoption is not only a regulatory requirement but an opportunity for businesses to modernise operations, improve cash flow, and secure a competitive advantage in the digital economy. By leveraging the insights provided, Malaysian businesses can confidently step into the future of digital invoicing, ready to reap the vast benefits it offers.
SwiF is Malaysia’s Leading-Edge B2B2C Fintech Solution.
Powered by Syntrino Solutions, Southeast Asia’s leader in supply chain management, SwiF provides your business with both a payment gateway and an innovative e-invoicing plug-in that can be used on its own or integrated to your existing accounting system.
It allows you to seamlessly upload your documents to the LHDN system for validation and automatically prints the Unique Identification Number on the invoice along with the QR code as proof of validation. The validated e-invoices is then ready to be shared with your customers. The embedded SwiF payment link allows your customers to make direct payment through our payment gateway by selecting their preferred payment method. SwiF ensures both data security and seamless integration.
Contact our team for more information on how SwiF can help your business embrace the e-Invoice mandate.